ICHTHYOSIS
Ichthyosis is derived from the Greek word “ichthys” meaning “fish”. It is a skin disorder in which there is formation of dry, thickened, scales or flakes on the skin, which appears like fish scales.
The condition often begins in early childhood and is usually life long.
Types of ichthyosis:
The most common types of ichthyosis are:
- Ichthyosis vulgaris- Ichthyosis vulgaris is commonly observed in most people. It accounts for about 95% of all ichthyosis cases
- Lamellar ichthyosis
- Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis
- X-linked ichthyosis.
Causes of ichthyosis:
- It is seen to be a Genetic disorder that is passed from parent to child or that occurs spontaneously.
- Use of harsh soaps or detergents make the skin dry and are known to cause ichthyosis.
- Cold weather is also an important factor which increases dry skin and leads to ichthyosis.
- Certain soaps or lotions containing certain scents or perfumes may also trigger this.
- Acquired ichthyosis is not inherited and occurs for the first time in adulthood. It is usually associated with some general systemic diseases, such as under active thyroid, sarcoidosis, lymphoma, generalized cancer or HIV. It may be provoked by certain medications (such as kava, nicotinic acid and hydroxyurea).
Signs and Symptoms of Ichthyosis
Sign and symptoms may include the following:
- Itching of skin.
- Dry skin, scaling and flaking of skin.
- Mild itching.
- Body odor.
- Thick scales and cracks.
- Rough skin.
- Overheating: ichthyosis may affect normal temperature control by reducing the ability to sweat
- Limited movement: dry, scaly skin may make it too painful to move some parts of the body
- Secondary infection: cracking and splitting of the skin may lead to skin infections and sometimes systemic infections
- Impaired hearing or eyesight: Excessive skin may build up over the ears or eyes causing partial deafness or blurred vision.
Diagnosis of ichthyosis:
Diagnosis of ichthyosis:
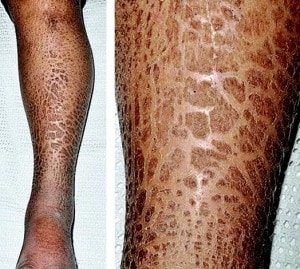 Often a physician is able to diagnose ichthyosis by examining the skin. A family history if available is useful. In some cases, a skin biopsy is done which is confirmatory.
Often a physician is able to diagnose ichthyosis by examining the skin. A family history if available is useful. In some cases, a skin biopsy is done which is confirmatory.
Treatment for Ichthyosis
Ichthyosis can be treated, but it cannot be cured. The treatments are designed to relieve the symptoms. Common treatments consist of moisturizing and exfoliating the skin. This helps prevent dryness, reduce scaling, cracking and build-up of skin.
Conventional Treatment may include:
Use of moisture-retaining creams or ointments such as Petrolatum, lanolin or urea-containing preparations after a bath or shower helps in maintaining the skin moisture.
Retinoid is also used for some conditions.
Sometimes exposure to sunlight can improve the condition.
If there is the skin infection or in the case of body odor, timely use of antibiotics is helpful.
An auxiliary line of treatment:
- Avoid taking hot baths or showers as they dry out the skin and use lukewarm to cool water. Soap should not be used on the affected skin because it irritates and dries the skin. One can use the soap substitute Cetaphil lotion which is available from the pharmacy without a prescription.
- Avoid rubbing the skin dry after you bathe.
- Living in a warm climate often improves ichthyosis.

