CELLULITIS
Introduction:
Cellulitis is an acute or chronic inflammation of the connective tissue of the skin, caused by infection with a type of bacteria (Staphylococcus, Streptococcus or other bacteria).
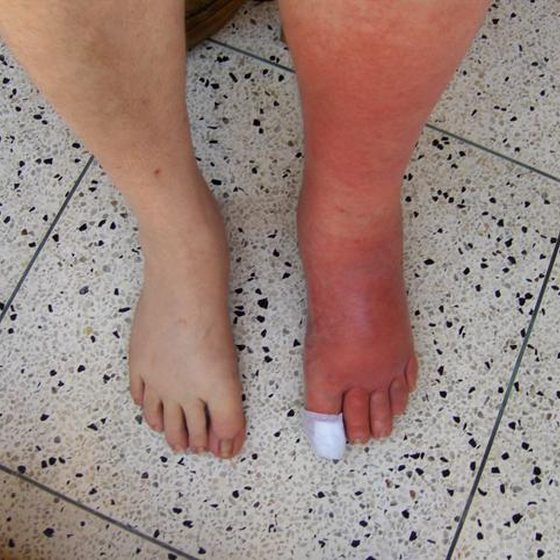
Cellulitis frequently occurs on exposed areas of the body such as the arms, legs, and face. It is characterized by redness, swelling, warmth and pain or tenderness.
The swelling can spread rapidly.
Causes:
Cellulitis occurs when the bacteria enter through a break in the skin. This break need not be visible to the naked eyes. Group A Streptococcus and Staphylococcus are the most common bacteria which can cause cellulitis. Predisposing factors for cellulitis include insect bites, animal bites, itchy (pruritic) skin rash, recent surgery, athlete’s foot, dry skin, eczema, burns and boils, lymphedema swelling, diabetes, patients on immunosuppressive or corticosteroid medications, etc.
Symptoms:
The affected area is red due to the inflammation and there may be warmth over it. Tight, glossy, “stretched” appearance of the skin is commonly seen. Pain or tenderness of the affected area is also seen. Other symptoms that may be seen include fever (with or without chills), sweating, fatigue, muscle pains (myalgia) and malaise. Occasionally, local lymph nodes may be swollen.
Self-care for Cellulitis Patients:
Rest the affected part of the body
Elevate the infected area to decrease the swelling and to relieve the discomfort.

