CROHNS DISEASE
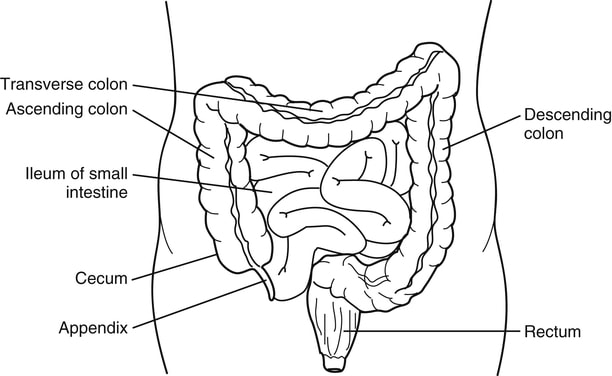
Crohn’s disease is included in a group of disorders termed as Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD). The other disease included in this group is Ulcerative Colitis. IBD occurs when the immune system contributes to damage to the gastrointestinal (digestive) tract by causing inflammation. Crohn’s disease causes inflammation, deep ulcers and scarring in any portion of the digestive tract from mouth to anus; however, it is most commonly seen in the last part of the small intestine called the terminal ileum and the caecum.
Causes:
Crohn’s disease is a rare disorder that has auto-immunity playing an important role in its initiation. A genetic component has been suggested to cause this condition.
Symptoms:
Crohn’s disease is a systemic disease, hence apart from gastrointestinal symptoms, it can also cause complications outside of the gastrointestinal tract. The main gastrointestinal symptoms are abdominal pain and diarrhea, which may be bloody. Weight loss is commonly seen in many patients. Flatulence, bloating, pain and/or itching around the anus is also observed by some patients. Some rare symptoms are difficulty in swallowing, upper abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Symptoms outside the gastrointestinal tract include skin rashes, arthritis, fever, anemia, ophthalmic involvement, osteoporosis, ulcers in the mouth, growth retardation in children, etc.

